How to Calculate and Solve for Linear Expansivity, Area Expansivity and Volume or Cubic Expansivity
Last Updated on February 13, 2024
Linear expansivity, area expansivity and volume or cubic expansivity are all parameters that are being governed by heat energy. All three parameters are dependent on temperature rise which is primarily in Celsius unit of temperature.
Linear expansivity additionally depends on the original length and final length, area expansivity additionally depends on the original area and final area and lastly, cubic or volume expansivity depends on the original volume and final volume.
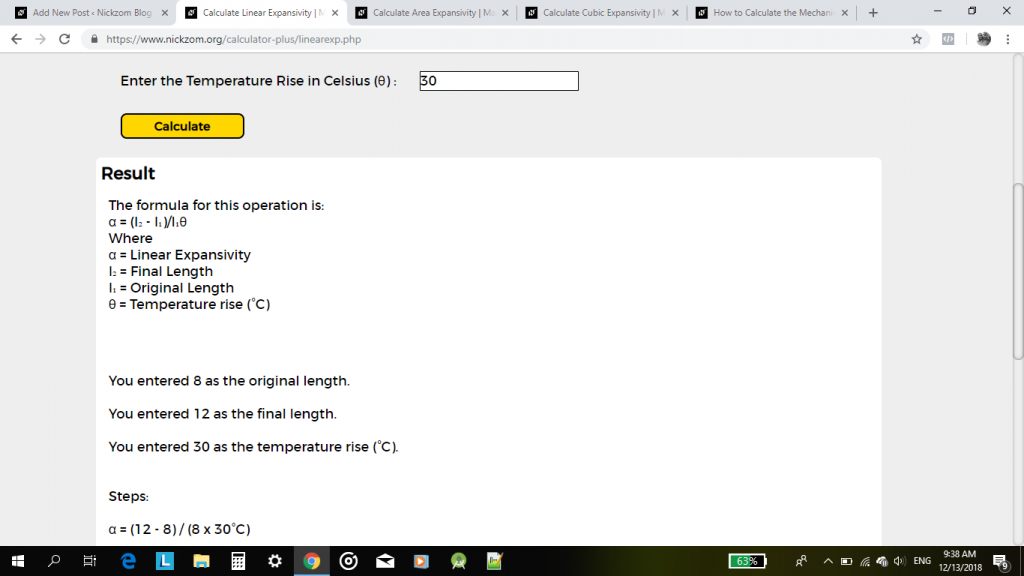
The formula for calculating linear expansivity is (l2 – l1) / l1θ
l2 represents the final length.
l1 represents the original length.
θ represents the temperature rise in Celsius.
The formula for calculating area expansivity is (A2 – A1) / A1θ
A2 represents the final area.
A1 represents the original area.
θ represents the temperature rise in Celsius.
The formula for calculating volume or cubic expansivity is (V2 – V1) / V1θ
V2 represents the final volume.
V1 represents the original volume.
θ represents the temperature rise in Celsius.
Let’s solve three examples on linear expansivity, area expansivity and volume or cubic expansivity respectively. The Calculator Encyclopedia (Nickzom Calculator) is capable of solving for these parameters showing the formula workings and answer accurately.
Access Nickzom Calculator to Solve Linear Expansivity, Area Expansivity and Volume or Cubic Expansivity
First and Foremost, one needs to have access to Nickzom Calculator via any of these means:
- Web – https://www.nickzom.org/calculator-plus
- Android (Paid) – https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.nickzom.nickzomcalculator
- Apple (Paid) – https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/nickzom-calculator/id1331162702?mt=8
Then, proceed to the Calculator Map, click on Heat Energy under the Physics section
Example 1:
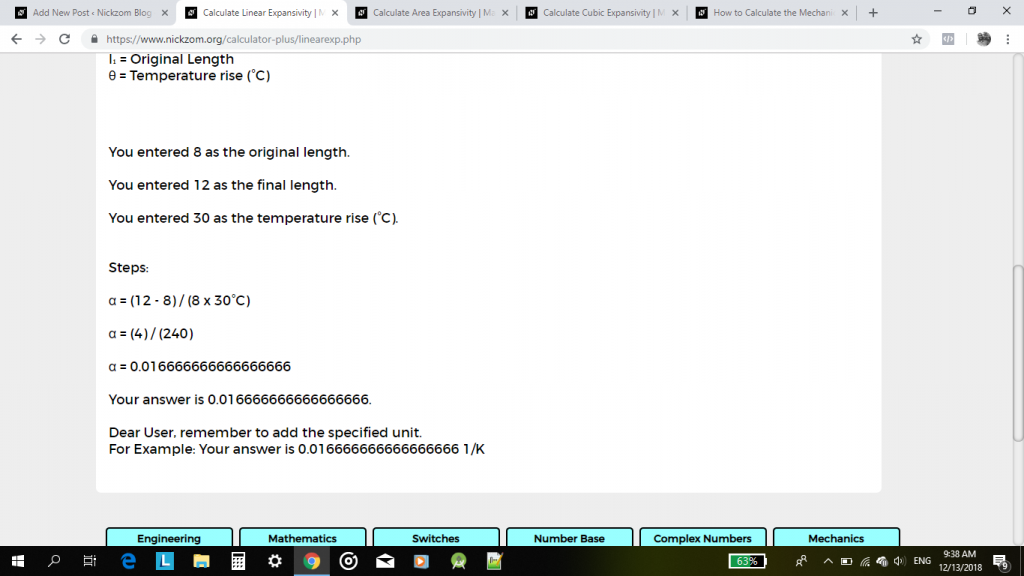
Find the linear expansivity (α) of a metal where its original length is 8 cm and its final length is 12 cm after undergoing a rise in temperature of 20°C.
α = (l2 – l1) / l1θ
Where:
l2 (Final Length) = 12 cm
l1 (Original Length) = 8 cm
θ (Temperature Rise) = 20°C
Therefore,
α = (12 – 8) / 8(20) 1/°C
α = 4 / 160 1/°C
Then, α = 0.025 1/°C
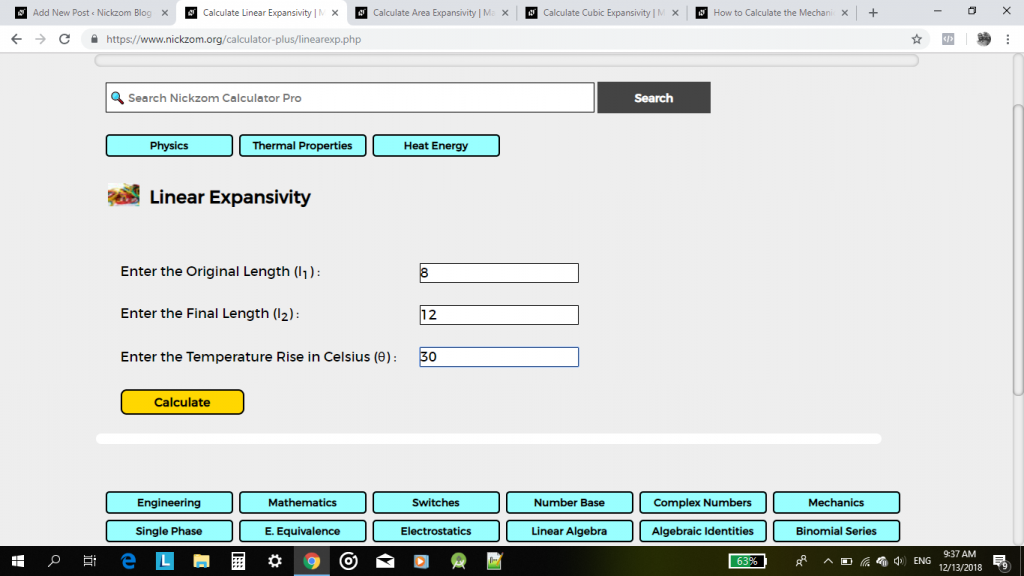
Using Nickzom Calculator, click on Linear Expansivity,
Then, enter your values appropriately and accurately
Lastly, click on the Calculate Button
Example 2:
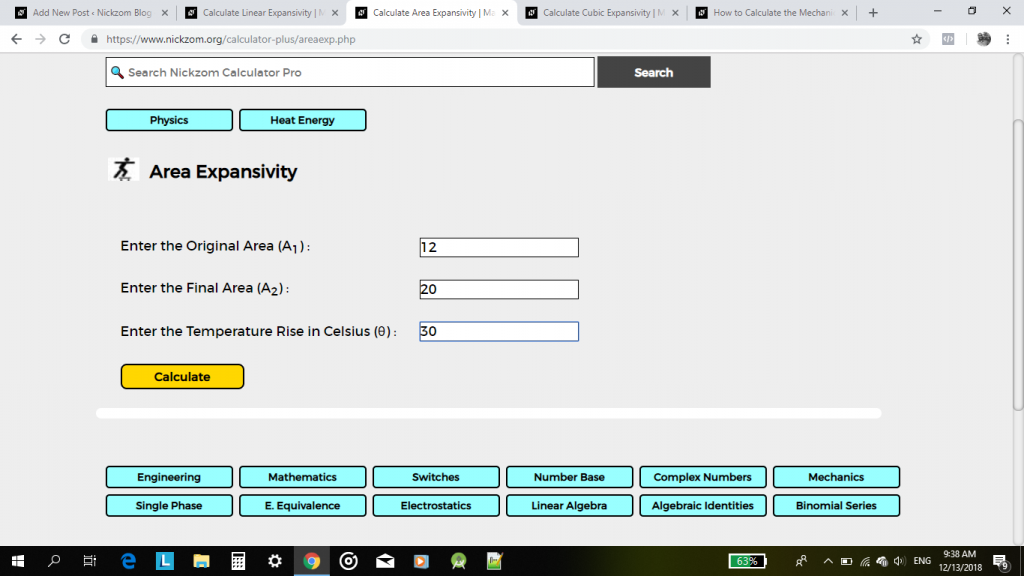
Find the area expansivity (β) of a metal where its original area is 12 cm² and its final length is 20 cm² after undergoing a rise in temperature of 30°C.
β = (A2 – A1) / A1θ
Where:
A2 (Final Area) = 20 cm²
A1 (Original Area) = 12 cm²
θ (Temperature Rise) = 30°C
Therefore,
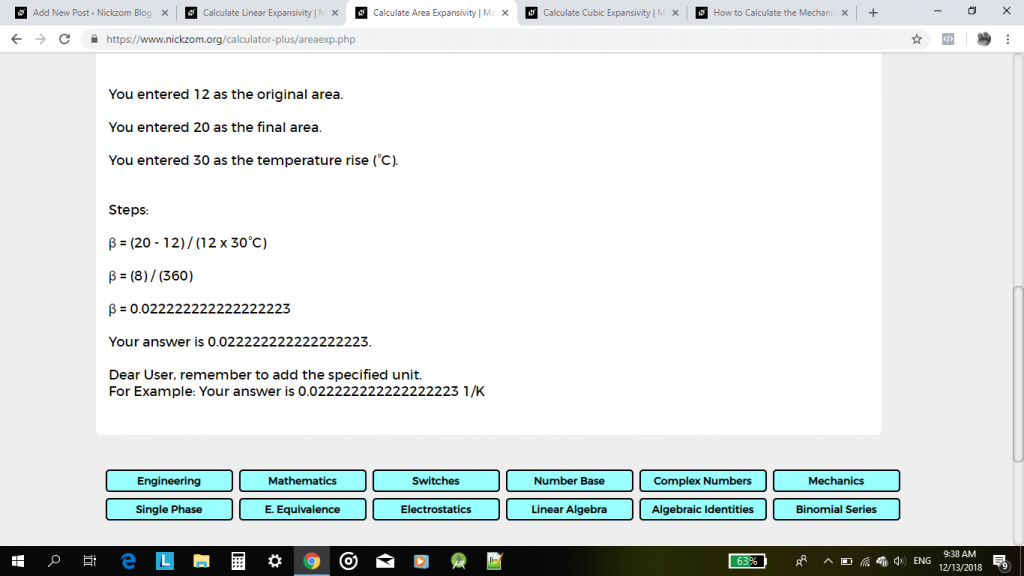
β = (20 – 12) / 12(30) 1/°C
β = 8 / 360 1/°C
That is, β = 0.02222 1/°C
Using Nickzom Calculator, click on Area Expansivity,
Then, enter your values appropriately and accurately
Lastly, click on the Calculate Button
Example 3:
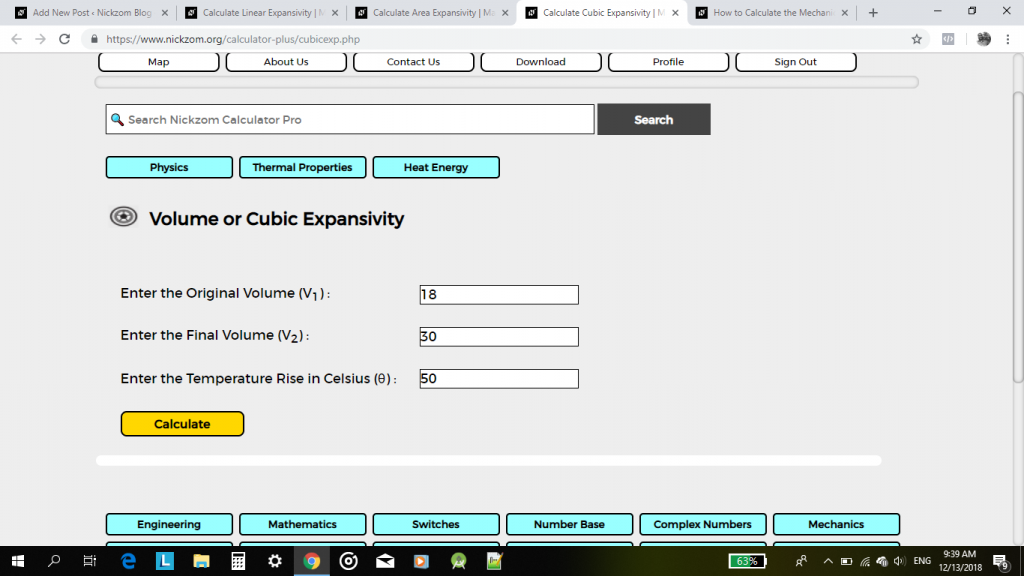
Find the volume or cubic expansivity (γ) of a metal where its original volume is 18 cm³ and its final length is 30 cm³ after undergoing a rise in temperature of 50°C.
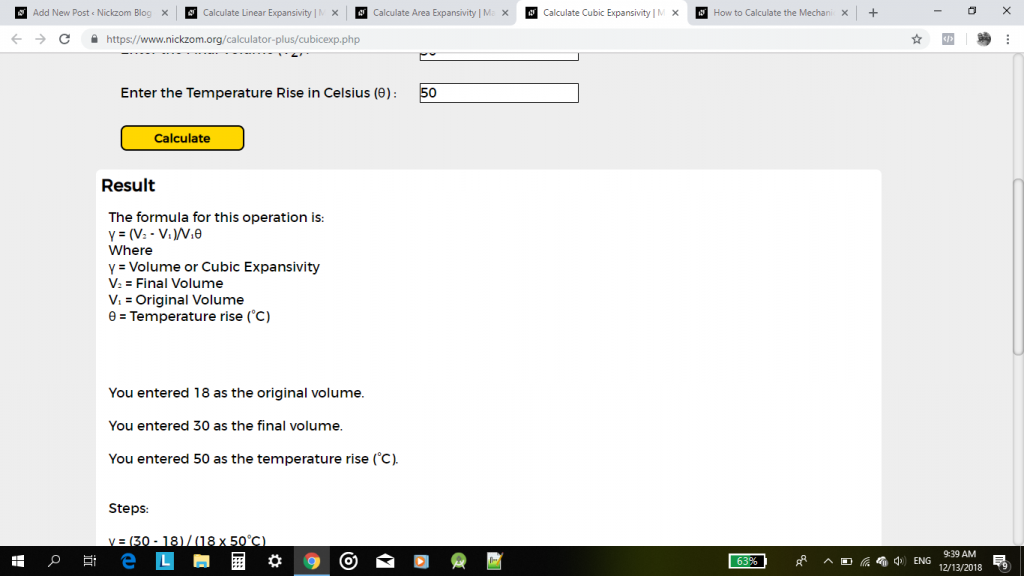
γ = (V2 – V1) / V1θ
Where:
V2 (Final Volume) = 18 cm³
V1 (Original Volume) = 30 cm³
θ (Temperature Rise) = 50°C
Therefore,
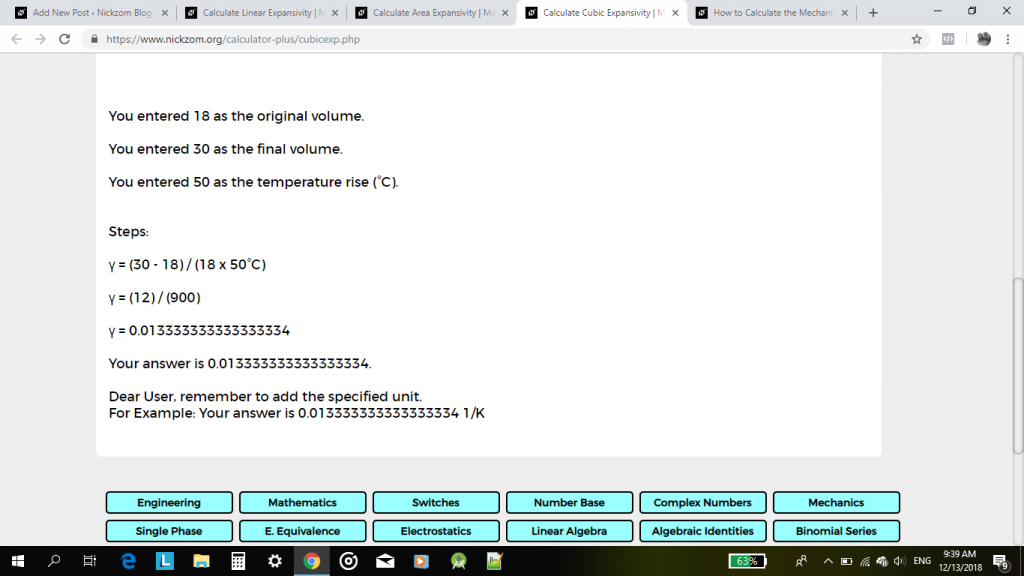
γ = (30 – 18) / 18(50) 1/°C
γ = 12 / 900 1/°C
Therefore, γ = 0.01333 1/°C
Using Nickzom Calculator, click on Volume or Cubic Expansivity,
Then, enter your values appropriately and accurately
Lastly, click on the Calculate Button